The Australian Dietry Guidelines
| Food Group | Women (aged 19 – 50) | Men (aged 9 – 50) |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables and legumes | 5 serves per day | 6 serves per day |
| Fruit | 2 serves per day | 2 serves per day |
| Cereals and staples | 6 serves per day | 6 serves per day |
| Protein from lean meat, fish, poultry, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes and beans | 2.5 serves per day | 3 serves per day |
| Dairy or dairy alternatives | 2.5 serves per day | 2.5 serves per day |
In addition to this the guidelines state to use small amounts of added fats and limit processed foods and beverages to occasional intake and in small servings.
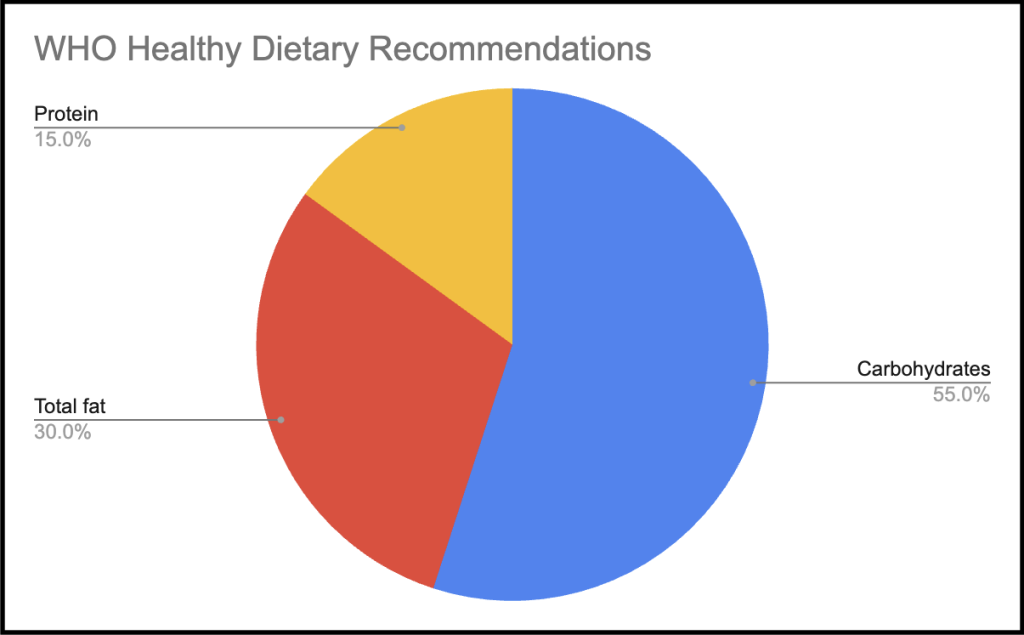
The World Health Organisation (WHO) aims to provide guidelines to support good health and monitor health trends. WHO provides evidence based recommendations that are applicable worldwide taking into account availability, food culture and economy (Saluja et al, 2022). Table 2 shows the WHO recommendations for individuals aged 10 and over based on a daily intake of 2,000 calories.
| Food Group | WHO Recommendation for daily intake |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, whole grains and pulses | 45 – 75% 25 grams of fibre 400 grams, combined, of fruit and vegetables |
| Proteins | 10-15% |
| Fats | 15-30% Focus on unsaturated fats (fish, avocado, nuts and sunflower, canola, soybean and olive oil. Less than 10% from saturated fats (animal fats) Less than 1% from trans fats (found in processed foods as chemically altered fats used mainly to extend shelf life or stabilise the texture of a food item. |
| Salt | Less than 5 grams |
| Sugar | Less than 50 grams (12 teaspoons) of added sugar |